Architectural visualization, commonly known as ArchVIZ, is a process that combines 3D modeling and artificial lighting to create realistic images of buildings and spaces. This article provides a detailed explanation of the ArchVIZ process and how it’s used in architecture.
Architectural visualization is a rapidly evolving field that demands a wide range of skills and knowledge in areas such as design, lighting, texturing, and programming. This article will cover the basics of ArchVIZ and how it can be utilized to create lifelike images of buildings and spaces.
What is ArchVIZ?
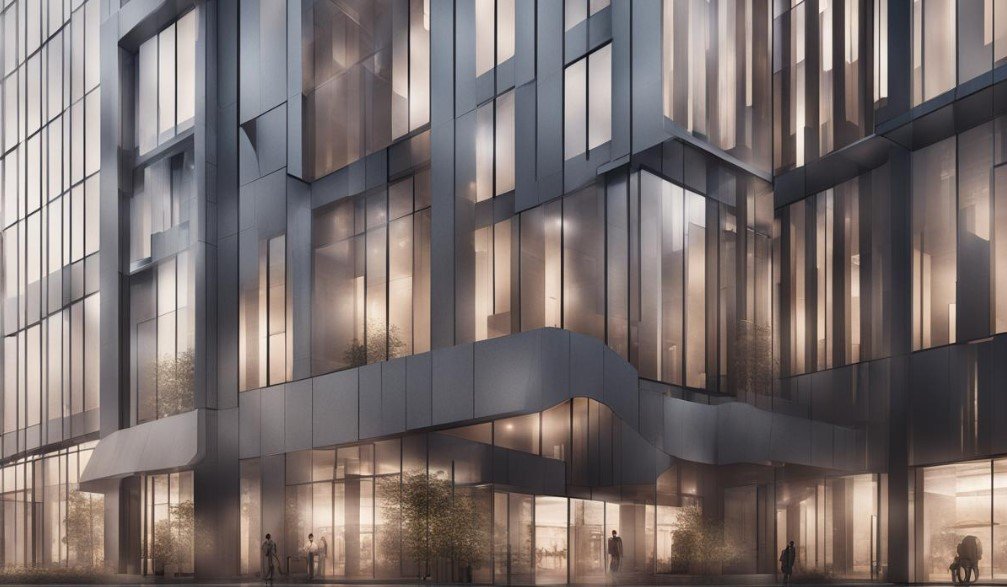

ArchVIZ, short for Architectural Visualization, is a technique used to create highly realistic images of architectural designs using 3D modeling software. The goal is to produce photorealistic images without the need for post-editing.
Architectural visualization focuses on presenting projects in an appealing and convincing way, allowing clients, investors, and stakeholders to better understand the design and its impact on the environment. ArchVIZ is a powerful tool to communicate the architect’s vision and convey the essence of the project effectively.
Differences Between ArchVIZ and Rendering
While both terms involve creating realistic images, there is a fundamental difference between ArchVIZ and rendering. The main distinction lies in the process used to generate the images. Rendering typically involves using post-production tools to enhance the image, whereas ArchVIZ relies exclusively on the software’s capabilities to produce the final result.
In other words, rendering is a more labor-intensive and flexible process, allowing users to intervene in the image and make adjustments afterward. On the other hand, ArchVIZ is a more automated and faster process, relying on the software’s capabilities to generate realistic images without human intervention.
Examples of ArchVIZ Results
Unreal Engine 4 is a popular tool used for architectural visualization and has produced impressive results in this field. Unreal Studio, a new tool launched by Unreal Engine, is specifically designed for architectural visualization, offering improvements in efficiency and collaboration.
For example, the architectural design studio Foster + Partners used Unreal Engine 4 to create a promotional video for the new Apple Park building. The result was a realistic video showcasing both the interior and exterior of the building, allowing viewers to experience the feeling of being inside the space.
How to Get Started with ArchVIZ

To create ArchVIZ, you’ll need to use 3D modeling software like Unreal Engine or similar tools. Datasmith, a plugin for Unreal Engine, allows you to import model data from other 3D modeling programs quickly and easily, streamlining the workflow.
Once you have the software installed, you should learn to use its tools and features. Unreal Engine, for instance, offers a wide range of tools for creating realistic textures, lighting, and visual effects. Learning to use these tools will allow you to create more detailed and realistic images.
With experience in using the software, you can start creating your own ArchVIZ images. Begin with a simple project, like a house or building, and then move on to more complex projects. Practice is the best way to enhance your skills and master the software’s tools.
Datasmith: A Plugin for Unreal Engine
Datasmith is a plugin for Unreal Engine that enables the import of 3D models from other 3D modeling programs, facilitating ArchVIZ work. With Datasmith, you can import models from Autodesk Revit, SketchUp, Blender, and other popular formats, and then use them directly in Unreal Engine to create architectural visualizations.
One of Datasmith’s most valuable features is its ability to maintain the integrity of the original model while importing it into Unreal Engine. This means you can preserve all the details and information associated with the model, such as materials, textures, and other attributes, without losing anything in the import process.
BIM (Building Information Modeling): An Essential Tool in Architecture
BIM is a collaborative working methodology that centralizes all project information (geometric, temporal, cost-related, environmental, and maintenance-related) in a digital model. It is an essential tool for architects, engineers, and construction professionals.
This digital representation of the building allows for better communication among team members, improved decision-making, and enhanced collaboration throughout the entire project lifecycle. By using BIM, architects can create detailed models that include not only the physical structure but also its functional and operational aspects. This enables them to simulate and analyze various scenarios, making it easier to identify potential issues and optimize the design.
BIM is particularly useful in ArchVIZ, as it allows for the creation of highly accurate and detailed 3D models that can be used to generate photorealistic images. By integrating BIM with ArchVIZ, architects can create a comprehensive digital representation of their project, which can be shared with clients, stakeholders, and other team members.
Conclusion
ArchVIZ is a powerful technique that combines 3D modeling with visualization to create realistic and appealing images of architectural projects. While it may seem intimidating at first, the ArchVIZ process becomes more accessible thanks to tools like Unreal Engine and Datasmith.
The importance of ArchVIZ in the architectural industry cannot be understated. It allows architects and designers to present their projects effectively, influencing decision-making by clients and stakeholders. Additionally, ArchVIZ can be used to create immersive and realistic experiences for visitors of buildings and public spaces, enhancing their perception and appreciation of architectural design.
Free Revit families on Bimshares.com
Power by Baugam