The best free Revit families in one place
Download Revit families for free and test the quality of our BIM components. Search, select and download!





Unlock the 9 download limit per day by becoming a member
All BIM content is compatible with your favorite rendering software!
What is Bimshares?
Bimshares is a company that seeks to digitize physical products and connect designers with manufacturers.
Education focused on building the METAVERSE
Companies that support us
What is a parametric family?
A parametric family or also called parametric component is an intelligent 3D model that adapts to the measurements and changes of a project. These parametric characteristics are thanks to good BIM modeling.
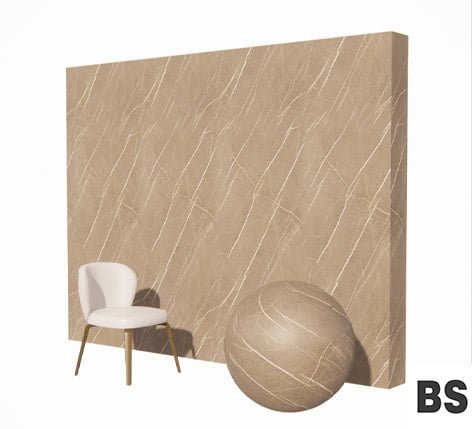
Download PBR textures for free
Manufacturers support Bimshares, download the best free PBR textures ready to apply with one click in the best rendering software.





Download more than 2000 parametric families totally free, without downloading any programs.
We know that content must be free, easy to access and for massive use. At Bimshares we seek to provide you with more and more parametric content and the best BIM files.
Get your projects done in record time

1 - Download your RVT files
More than 1000 files available in the best quality.
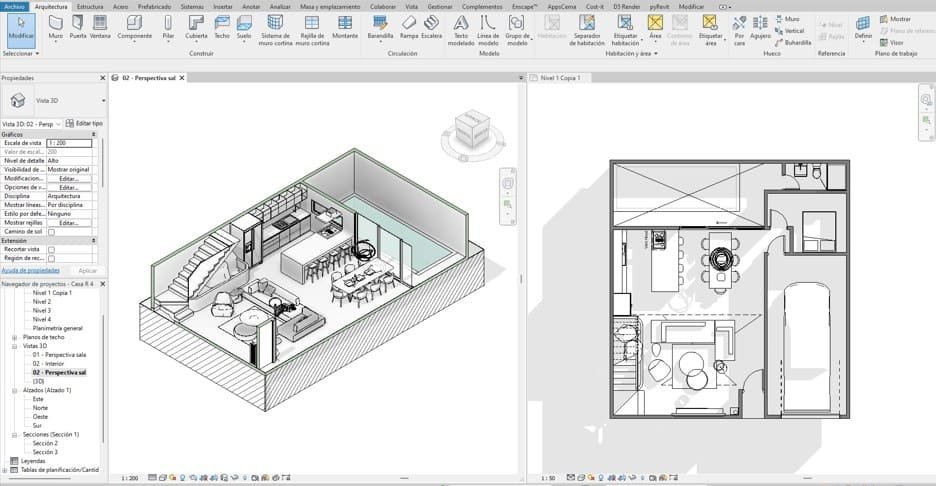
2 - Download your RVT files
Change the size of measurements, scale and materials with a single click.
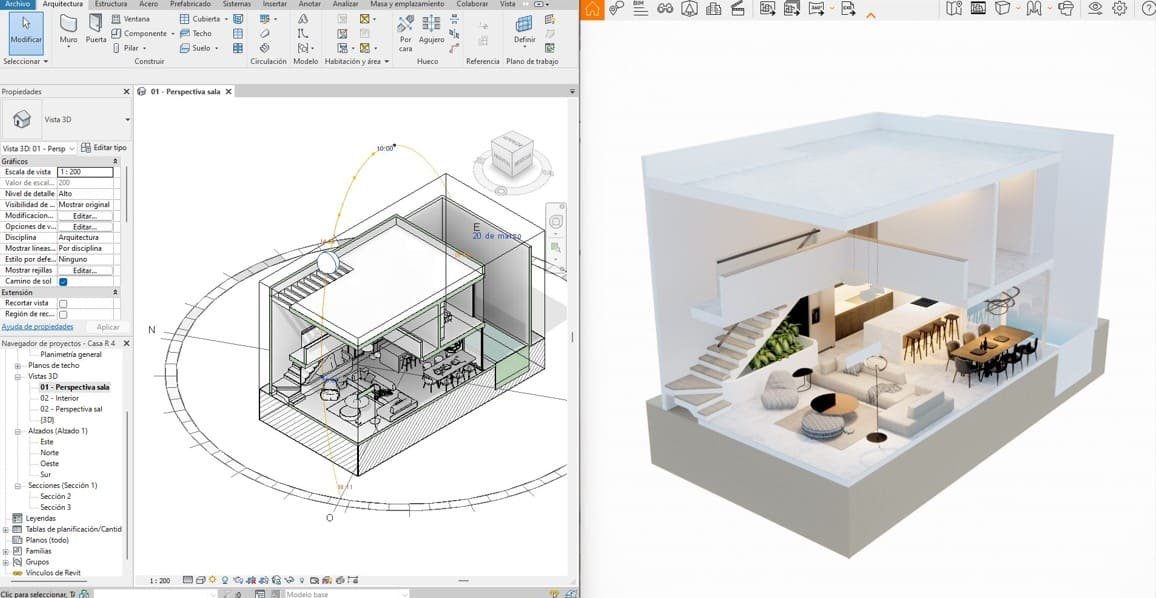
3 - Study your project
With our parametric models you can see your designs in real time.
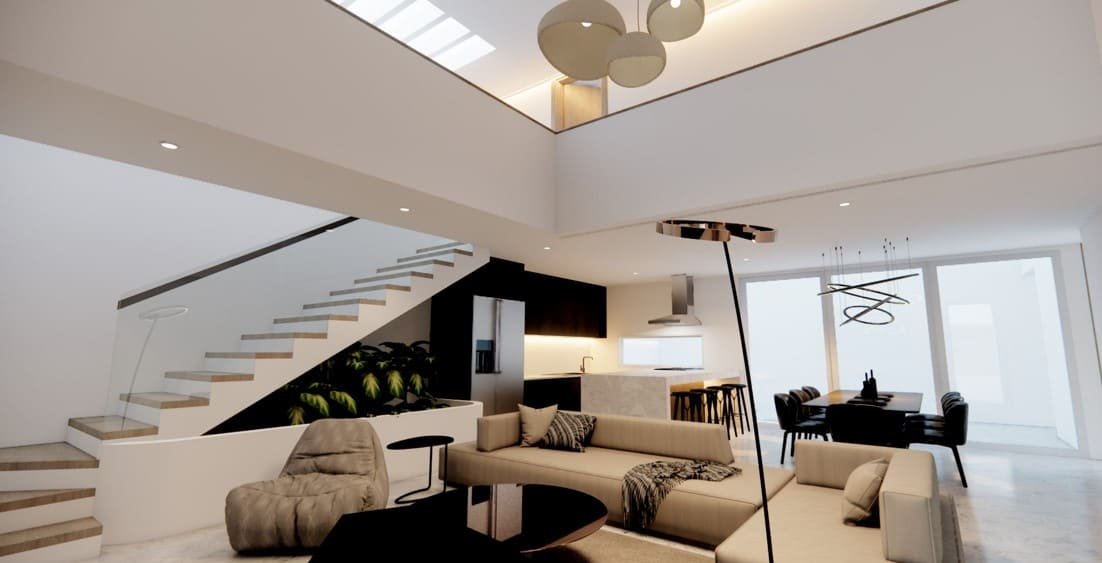

4 - Rendering
Finish your projects in record time, you don't need to waste hours modifying materials or creating furniture. At Bimshares we have it all.